
October is fast slipping through my fingers. This month Han and I celebrated the second anniversary of our wedding ceremony, but unfortunately we also had to farewell my dearly beloved grandmother, which has always been so unimaginable for me that it still doesn’t feel real. Alice is now 18 months and has started jumping on the bed and is simply thriving. Singing, dancing, chatting with anyone who will smile back at her. I will be discussing her progress in Korean language in an upcoming post.
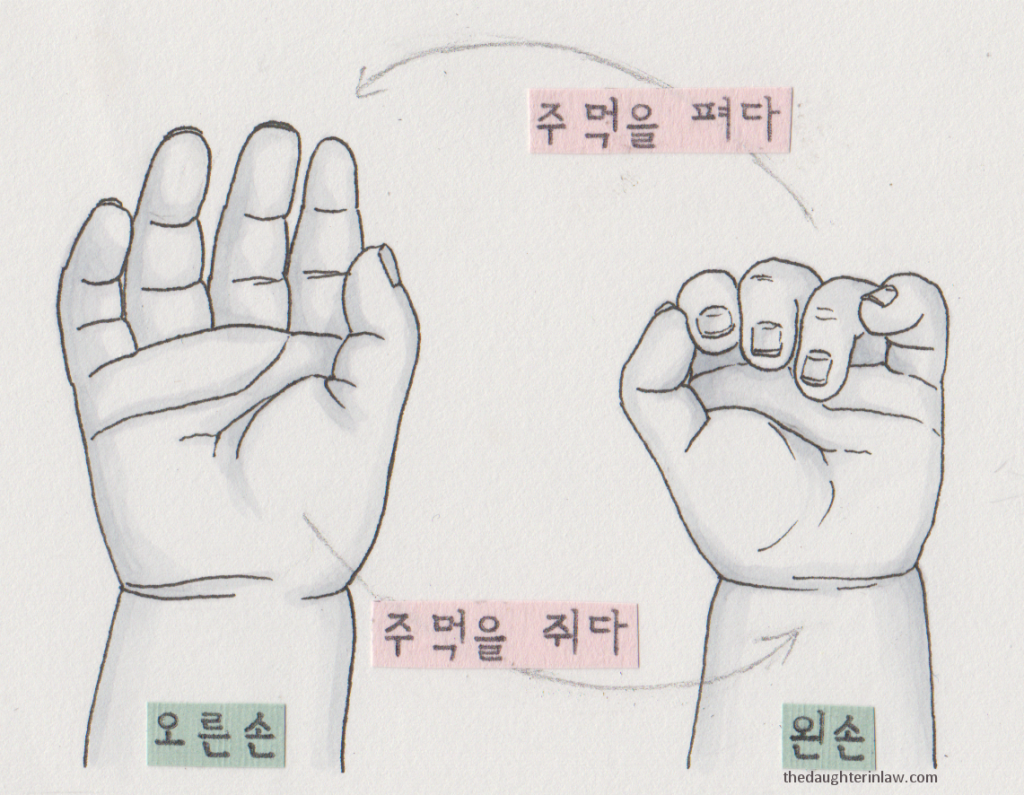
I thought I might provide some more detailed vocabulary relating to hands. If there is one major difference between learning Korean to make friends, and learning Korean to use with a baby, it’s that for speaking with a baby you need a name for EVERYTHING. If you can see it, if you can hear it, smell it, taste it, feel it, experience it, if you can hurt it, it needs a name, and babies are particularly curious, exploring everywhere, always looking back to you to explain the interesting and new.

There are several different sets of names for the fingers. I’ve included two (so those in cream and pink are each a set, not left or right specific)


 Since Alice is competent at bowing her head to greet and thank people, I recently taught her to “배꼽인사” (belly button bow)
Since Alice is competent at bowing her head to greet and thank people, I recently taught her to “배꼽인사” (belly button bow)